The Bradford Factor Formula Explained for UK Managers
Posted by Robin on 23 Jan, 2026 in
So, what exactly is the Bradford Factor formula? Think of it as an HR tool designed to put a number on the disruption caused by staff absence. It specifically zooms in on a particular problem: frequent, short-term absences are almost always more chaotic for a business than longer, planned periods of leave.
The formula helps managers spot problematic attendance patterns that might otherwise fly under the radar if you were just counting the total number of sick days.
What Is the Bradford Factor and Why Does It Matter?
Let's paint a picture. You're running a small team and have two employees.
Employee A needs a minor operation and is off for a single, continuous two-week period. You know about it in advance, so you can arrange cover and shuffle schedules around. It's an inconvenience, but manageable.
Now, consider Employee B. They are also absent for a total of ten days, but it’s spread across ten separate, unplanned Mondays throughout the year. Which of these two scenarios gives you a bigger headache?
If you’re like most managers, Employee B's sporadic absences are far more disruptive. Each unexpected no-show forces you to reshuffle tasks at the last minute, throws team workflow into disarray, and puts a recurring strain on their colleagues. This is precisely the issue the Bradford Factor was created to measure. It’s not just about how many days someone is off, but how often.
The core idea is simple yet powerful: frequent, short, and unplanned absences create significantly more operational friction than longer, single spells of leave. The formula quantifies this disruption with a numerical score.
This distinction is crucial for keeping productivity and service delivery on track. It’s like the difference between a planned two-week factory shutdown for maintenance and ten random, unannounced one-day shutdowns throughout the year. The first is a manageable project; the second is a logistical nightmare.
Before we get into the nitty-gritty of the calculation, here’s a quick overview of what the Bradford Factor is all about.
The Bradford Factor at a Glance
| Concept | Description |
|---|---|
| What It Is | A mathematical formula used in HR to measure the disruptiveness of employee absenteeism. |
| Primary Purpose | To highlight the impact of frequent, short-term absences over longer, single periods of leave. |
| Key Components | The formula uses two main variables: the total number of absence instances (spells) and the total number of days absent. |
| The Score | It generates a numerical score. A higher score indicates a more disruptive pattern of absence. |
| Application | Used as a trigger point for conversations, not as a standalone disciplinary tool. |
This table sets the stage, but the real value comes from understanding how to use the score to support your team effectively.
Identifying Disruptive Patterns, Not Just Counting Days
The Bradford Factor encourages a shift away from just tallying up sick days. It gives you a much more nuanced view of attendance, acting as an objective indicator that flags patterns worthy of a supportive conversation with an employee.
It helps managers start asking the right questions:
- Is there an underlying wellbeing issue we need to address?
- Are certain teams struggling with higher rates of disruptive absence than others?
- Is our current absence policy actually supporting both our people and the business effectively?
By focusing on the frequency of absence, the formula gives you a consistent starting point for these important discussions. This is especially vital when you look at the bigger picture. In the UK, sickness absence costs businesses an estimated £16 billion annually, making effective absence management a top priority. You can learn more about the financial impact of absenteeism and find additional insights on Hibob.
This huge cost really underlines why tools that pinpoint the most disruptive patterns are so valuable for UK organisations. The Bradford Factor formula provides exactly that focus.
How to Calculate Scores with the Bradford Factor Formula
At its heart, the Bradford Factor formula is a simple piece of maths designed to give more weight to frequent, short-term absences compared to a single, longer period off. It might look a bit clinical at first glance, but once you break it down, it's actually quite straightforward.
The formula itself is written as: B = S² x D
Let's unpack what each letter means so you can calculate scores with confidence. Getting to grips with these basics is the first step to using the tool fairly and effectively.
- B is the final Bradford Factor Score. This is the number that helps you spot potential absence patterns that need attention.
- S stands for "Spells" – the total number of separate instances of absence. It’s crucial to remember that one continuous period of sick leave counts as just one spell, no matter how many days it lasts.
- D is the total number of Days an employee was absent within a set period.
This "set period" is typically a rolling 52-week window. This ensures the score always reflects the most recent year of an employee's attendance, keeping the data relevant.
Seeing the Components in Action
The real magic – and what gives the formula its punch – is the "S²" part. Squaring the number of spells is what gives it that exponential weighting. Someone with a single, long-term absence will have a low 'S' value, and therefore a low score. On the other hand, an employee with lots of little absences will see their 'S' value shoot up, causing their final score to skyrocket.
This infographic paints a clear picture of how different absence patterns translate into either low or high-impact scores.
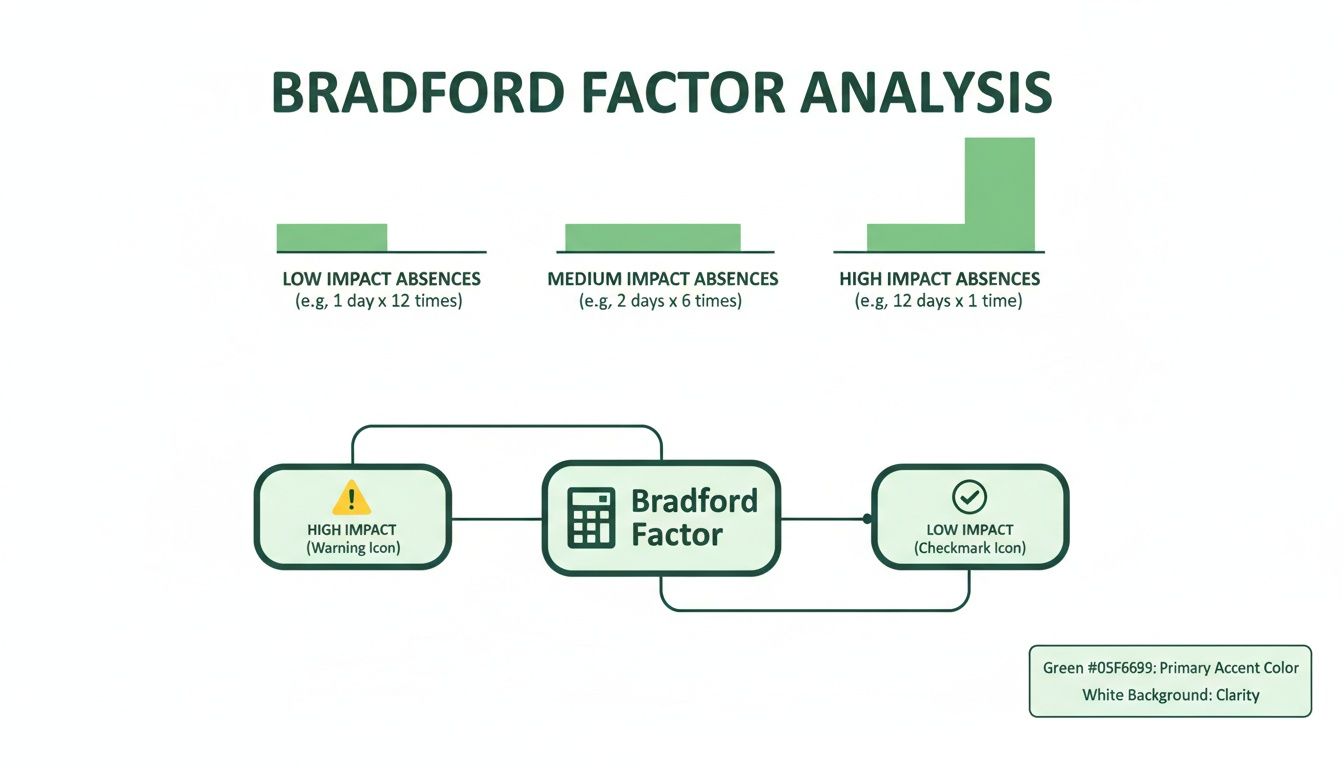
As the diagram shows, one long absence has a low impact, whereas multiple shorter ones are flagged as high impact, highlighting the potential disruption to the team.
This whole approach came out of research from the Bradford University School of Management back in the 1980s. The theory was simple: short, frequent, and unplanned absences are far more disruptive to a business than a single, planned or long-term one.
Worked Examples: Comparing Absence Scenarios
To really see how this plays out in the real world, let's compare two employees. We'll call them Anya and Ben. Both have been off work for a total of 10 days over the past year.
Scenario 1: Employee Anya
Anya had a nasty bout of flu and was off for 10 consecutive working days.
- Spells (S) = 1
- Days (D) = 10
- Formula: 1² x 10
- Anya's Bradford Factor Score = 10
Scenario 2: Employee Ben
Ben had five separate absences, each lasting for two days.
- Spells (S) = 5
- Days (D) = 10
- Formula: 5² x 10
- Ben's Bradford Factor Score = 250
The difference is striking. Both employees were off for the exact same number of days, yet Ben's score is 25 times higher than Anya's. This is a perfect example of how the formula pinpoints the more disruptive pattern of frequent, unplanned leave.
Of course, keeping track of all this data and running the numbers for an entire team can quickly become a major admin headache. For businesses needing extra support, a Human Resources Virtual Assistant can handle the administrative legwork of collecting and processing absence data. This ensures everything is accurate and frees up your managers to focus on having supportive conversations with their team members, rather than getting bogged down in manual calculations.
Interpreting Scores and Setting Fair Thresholds
So, you’ve run the numbers and you have a Bradford Factor score. But what does that number actually mean? On its own, a score is just a figure on a spreadsheet. To give it power, you need to wrap it in a clear, fair, and transparent framework. This is where your trigger-point system comes in.
Think of it as transforming raw data into an actionable absence management policy. You define specific score ranges that prompt different levels of response from managers, moving from a quiet word of support to more formal procedures. This ensures everyone is treated consistently based on the same objective information.
Crucially, these scores should be the start of a conversation, not an immediate disciplinary tool. It’s all about spotting a potential pattern early and offering support before a small issue snowballs into a larger problem.
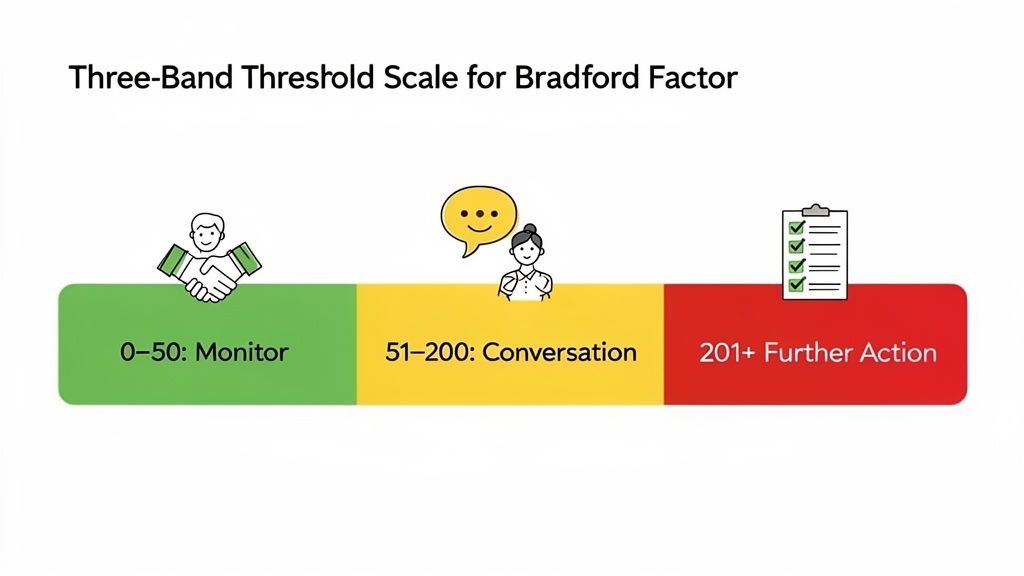
Establishing Your Company Thresholds
There isn’t a universal, one-size-fits-all set of Bradford Factor thresholds. Every organisation has its own pulse. What makes sense for a large manufacturing plant won't necessarily fly at a small creative agency. Your policy must be a reflection of your company culture, industry norms, and what the business genuinely needs to run smoothly.
That said, a typical tiered approach often looks something like this:
- Low Score (e.g., 0-50): This is the green zone. It generally signals no cause for concern and is typical for an employee with the odd, legitimate sickness day.
- Monitoring Range (e.g., 51-200): A score landing here is an early flag. It suggests a pattern of short, frequent absences might be starting to form, warranting some informal monitoring.
- Action Range (e.g., 201+): Once a score crosses this line, it usually triggers a formal process. This should always start with a supportive chat and only escalate if the pattern continues without improvement.
The real goal is to create a system that everyone understands. When your team knows what the thresholds are and what actions they trigger, the whole process feels less like a punishment and more like a predictable, fair part of managing attendance. Our in-depth guide to understanding your Bradford Factor score digs into more detailed examples.
A Bradford Factor score should be the beginning of a conversation, not the end of one. Its primary purpose is to help managers identify potential wellbeing issues and offer support before attendance problems escalate.
Using a trigger system is also your best defence against claims of bias. It helps managers apply the absence policy consistently across the board, which is absolutely essential for fairness.
From Score to Supportive Action
The moment an employee’s score crosses a trigger point, the focus must shift from the number to the person behind it. A high score is a signal, not a verdict. It’s a prompt for a manager to schedule a private, supportive conversation to find out what's really going on.
This table shows a common way to structure your actions based on different scoring bands.
Example Bradford Factor Thresholds and Actions
| Score Range | Interpretation | Recommended Action |
|---|---|---|
| 0 - 50 | No Concern | No action required. Standard return-to-work procedures apply. |
| 51 - 200 | Informal Concern | An informal, supportive chat to understand the reasons for the absences and check on the employee's wellbeing. |
| 201 - 400 | Formal Concern | A formal meeting to discuss the attendance pattern, documented with a verbal warning. The focus is on offering support and creating a plan for improvement. |
| 401 - 600 | Serious Concern | First written warning is issued. The conversation explores underlying issues and reiterates the impact on the team and business operations. |
| 601+ | Critical Concern | Final written warning or consideration of further disciplinary action, including potential dismissal, depending on the circumstances and previous actions. |
Remember, this is just a template. You need to customise these thresholds and actions to fit your organisation’s unique culture and policies. The most effective approach is always compassionate and focuses on finding solutions, whether that involves flexible working, wellbeing resources, or other forms of support.
The Pros and Cons of Using the Bradford Factor
The Bradford Factor formula is a powerful bit of kit, but like any tool, its usefulness is all in how you handle it. It gives you a clear, mathematical way to spot disruptive absence patterns, but it has zero understanding of the human stories behind the numbers. A balanced approach isn't just nice to have; it's essential.
If you understand its strengths and its weaknesses, you can build a fair and supportive absence management policy. The real goal is to use the data as a conversation starter, not as an automated disciplinary hammer.
The Advantages of the Bradford Factor
When you use it correctly, the Bradford Factor adds a welcome layer of objectivity and consistency to managing attendance. It shifts the focus from simply counting sick days to understanding their actual impact on your operations.
Here’s where it really shines:
Objective Measurement: The formula is pure maths. This means every employee's absence pattern gets the same treatment, taking subjective feelings from managers out of the initial picture. It creates a consistent, unbiased starting line for everyone.
Highlights Disruptive Patterns: This is its superpower. The formula is brilliant at telling the difference between a single, manageable long-term absence and a series of chaotic, short-term ones. This helps managers pinpoint the exact kind of absenteeism that throws a wrench in the works for team productivity and planning.
Simplicity and Clarity: The calculation itself, S² x D, is dead simple. This makes it easy for managers and HR teams to get their heads around, apply it consistently, and explain it to employees. It creates transparency about how attendance is being monitored.
The Disadvantages and Criticisms
For all its benefits, the Bradford Factor has some serious drawbacks. Critics quite rightly point out that its rigid, numerical logic can lead to unfair outcomes if it isn't tempered with a healthy dose of common sense and compassion. Its biggest flaw is that it completely ignores context.
The formula treats a day off for a pre-planned hospital appointment the same as a day off for a hangover. This lack of nuance is where the trouble starts, especially when you think about employee wellbeing and your legal duties.
A common—and entirely valid—criticism is that the Bradford Factor can end up penalising your most vulnerable employees. It doesn't know the difference between absences related to a protected characteristic, like a disability, and those that aren't.
This bluntness can cause some real problems:
Penalises Chronic Illnesses and Disabilities: Employees with long-term health conditions or disabilities often have frequent appointments or recurring short absences. The formula unfairly flags these people, which could easily lead to discriminatory practices if managers don’t apply discretion.
Ignores Mental Health and Caregiving: It takes no account of absences for mental health struggles or for caring responsibilities, like a child who is frequently unwell. A rigid application puts huge stress on employees who are already juggling difficult personal situations.
Encourages Presenteeism: Fearing a high score, employees might drag themselves into work when they're genuinely ill. This not only puts their own health at risk but also everyone else's, potentially spreading a minor bug through the entire team. This phenomenon, known as presenteeism, can actually damage productivity far more than the original absence ever would have.
Lacks Context: The score is just a number; it tells you nothing about the why. Was the time off due to a bereavement, a medical emergency, or even workplace stress? Without this context, the score is incomplete and can be seriously misleading.
At the end of the day, the Bradford Factor formula should never be used on its own. Relying solely on the score to take disciplinary action is a recipe for terrible morale, employee distrust, and potential legal headaches. It works best as one small part of a much bigger, human-first approach to managing absence. The number should trigger a supportive conversation, not an automatic warning letter.
Navigating Legal and Ethical Risks in the UK
The Bradford Factor formula can be a helpful tool for spotting absence patterns, but it's just that—a tool. Relying on it too rigidly, especially in the UK, can land your business in some serious legal and ethical hot water. The numbers don't understand context, compassion, or the law, and a misstep can quickly sour employee relations and even lead to a costly employment tribunal.
The biggest legal hurdle you need to be aware of is the Equality Act 2010. This legislation is designed to protect employees from discrimination based on "protected characteristics" like disability, age, or pregnancy. If your absence policy is driven purely by Bradford Factor scores, you could easily face claims of indirect discrimination.
Understanding the Equality Act 2010
Let’s take a real-world example. Imagine you have an employee with a long-term condition like Crohn's disease or multiple sclerosis, which is legally considered a disability. They might have frequent but short absences due to flare-ups or for hospital appointments. The Bradford Factor formula, with its focus on the frequency of absence, will flag this pattern and spit out a high score.
If a manager sees that high score and immediately starts disciplinary proceedings, the company is likely discriminating against that employee because of their disability. The law is very clear on this: employers have a duty to make ‘reasonable adjustments’ for disabled employees.
So, what do reasonable adjustments look like in practice?
- Discounting Disability-Related Absences: This is a big one. Time off for pre-planned hospital appointments or absences directly caused by a known disability shouldn't really be fed into their Bradford Factor score.
- Adjusting Trigger Points: For employees with known health conditions, it's often reasonable to set higher or more flexible trigger thresholds that take their personal circumstances into account.
- Modifying Duties or Hours: Sometimes a small change to someone’s role or work schedule can make a huge difference and reduce the need for absence in the first place.
This isn't just good practice; it's a legal requirement. The whole point is to ensure that disabled employees aren't unfairly penalised for circumstances beyond their control.
Data Privacy and GDPR Considerations
Remember, when you track employee absences, you're handling sensitive personal information. The reason for an absence is considered "special category data" under GDPR and needs to be handled with extra care.
You must have a clear, lawful reason for collecting and using this health data. Crucially, your team needs to understand exactly how their absence information is being used, including how it contributes to any Bradford Factor calculations. Transparency is absolutely vital for building trust and staying on the right side of the law. You can read more about the importance of accurate absence tracking for legal compliance in our dedicated guide.
The Bradford Factor formula should be a compass, not an anchor. It should point you towards a conversation, not hold you rigidly to a single, automated course of action.
Adopting a Human-Centric Ethical Approach
Beyond the strict letter of the law is the simple matter of good, ethical management. A high score should never be an automatic trigger for a formal warning. Think of it instead as a prompt—a reason to have a supportive, private chat with your employee.
This human-first approach reinforces that the Bradford Factor formula is just one piece of a much bigger picture. It's there to help you spot patterns, not to replace the need for skilled and empathetic management. The real goal is to understand the story behind the numbers and offer support. This builds a culture of trust where people feel safe enough to talk about their wellbeing without fearing automatic punishment.
Automating Bradford Factor Calculations with Leavetrack
Let's be honest: tracking absence spells and days manually in a spreadsheet is a recipe for a headache. It’s slow, fiddly, and wide open to human error. For any busy manager or HR team, trying to apply the Bradford Factor formula fairly using this method is a real uphill battle.
This old-school approach means you're always playing catch-up. It creates delays, inconsistencies, and a mountain of admin just to get a basic picture of attendance. By the time you spot a pattern, the moment to act has often already passed.

From Manual Spreadsheets to Smart Automation
This is where modern absence management systems like Leavetrack change the game entirely. Instead of managers getting bogged down updating spreadsheets, the system does all the heavy lifting for them. Instantly.
The moment an absence is logged, Leavetrack calculates the employee’s Bradford Factor score automatically and accurately. This simple shift transforms the entire process from a time-draining chore into an effortless, real-time part of your HR workflow. It frees up precious time, letting managers focus on supporting their teams instead of crunching numbers.
Setting Up Proactive Alerts and Thresholds
But the real power of automation isn’t just about saving time; it's about being proactive. Inside Leavetrack, you can plug your company's specific Bradford Factor thresholds directly into the system.
By setting custom trigger points, you transform the Bradford Factor from a backward-looking report into a forward-looking management tool. The system actively monitors scores and notifies the right people when action is needed.
This means you can set up automatic alerts that ping managers when an employee’s score crosses a certain point. For example, a score of 201 could trigger an immediate, private notification, prompting a manager to schedule a supportive check-in. This makes sure those important conversations happen promptly, consistently, and are always backed by objective data.
This proactive approach makes your absence policy far more effective and transparent. It helps you catch potential issues early, turning the theory behind the Bradford Factor into a practical and efficient management practice. You can learn more about how Leavetrack helps improve employee satisfaction by building fairer processes.
By automating the Bradford Factor formula, you give your managers the data they need, exactly when they need it, helping to create a more supportive and productive work environment for everyone.
The Bradford Factor: Your Questions Answered
Even when you've got your head around the formula, putting the Bradford Factor into practice can throw up some tricky questions. Let's walk through some of the most common queries that pop up for managers and HR teams.
How Often Does the Score Reset?
A Bradford Factor score isn't a black mark that follows an employee forever. It’s calculated on a rolling 52-week period.
Think of it like this: as a new week starts, the oldest week from a year ago drops off the record. This keeps the score current and relevant, focusing on recent attendance patterns. It gives people a genuine chance to improve and means old, resolved issues don't hang over them indefinitely.
Is the Bradford Factor Legal in the UK?
Yes, using the Bradford Factor formula is perfectly legal in the UK. Where you need to be careful is in how you apply it. Its use must always comply with employment law, especially the Equality Act 2010.
It's completely fine to use the score as a trigger for a supportive chat or as one part of a wider, consistent absence management policy.
The legal risks kick in if you use a high score as the only reason for disciplinary action, without digging into the employee's specific circumstances. This is especially critical if their absences are linked to a protected characteristic, like a disability.
Can Someone Be Sacked Just for a High Score?
A high Bradford Factor score on its own is almost never enough to justify a dismissal. A fair process always requires a proper investigation, clear warnings, and proof that you’ve looked at the individual's situation and offered support.
A consistently high score can certainly contribute to a dismissal decision, but only as one piece of a much larger puzzle. That puzzle would need to include:
- Records of formal warnings.
- Evidence of supportive conversations and any adjustments you offered.
- A clear failure to improve attendance even after you've tried to help.
So, What's a "Good" or "Bad" Score?
There are no officially mandated "good" or "bad" scores. It's up to each company to set its own thresholds.
That said, a score under 50 is generally seen as nothing to worry about. As a score approaches 200, it's often a good trigger for an informal chat. Anything significantly higher might be the point where you kick off a more formal process.
The most important thing is to clearly define these trigger points in your company's absence policy and apply them consistently to everyone. A "bad" score is simply one that crosses a line you've already drawn, signalling that it's time to have a conversation and understand what's really going on.
Ready to replace error-prone spreadsheets and automate your absence management? Leavetrack instantly calculates Bradford Factor scores, provides proactive alerts, and gives your managers the tools they need to support their teams effectively. Discover a smarter way to manage leave by visiting https://leavetrackapp.com.
