Boost HR Accuracy with the bradford formula
Posted by Robin on 11 Feb, 2026 in
The Bradford Formula is a straightforward calculation HR teams use to flag potentially disruptive patterns of short, frequent, and unplanned absences. Instead of just tallying up total sick days, it zeroes in on the operational impact of sporadic time off.
The formula itself is simple: S² x D (which stands for Spells squared, multiplied by Days).
What Is The Bradford Formula and Why Does It Matter?
Let's imagine you have two employees. Over the course of a year, both have been absent for a total of 10 working days. On paper, their impact looks identical. But this is where the Bradford Formula shows its real value—it reveals a crucial difference in how their absences affect your business and team morale.
Think of it as a tool designed to measure disruption.
One employee might have a single, two-week absence to recover from a planned medical procedure. It’s not ideal, of course, but the business can often see it coming. You can arrange cover, reshuffle workloads, and manage the situation. The disruption is contained.
Now, consider the second employee. They’ve also taken 10 days off, but as ten separate, single-day absences scattered across the year. Each absence is unplanned. Each one forces last-minute shift changes, stalls projects, and puts a recurring strain on their colleagues. This pattern is far more chaotic and, frankly, more costly to the business.
Uncovering Hidden Disruption
This is exactly what the Bradford Formula is designed to highlight. By squaring the number of absence instances (the 'spells'), it gives a much heavier weighting to frequent, short-term absences than it does to a single, long-term one.
The formula quickly distinguishes between a manageable, long-term absence and a chaotic pattern of frequent, unpredictable ones. This allows managers to move beyond a simple day count and address the root causes of operational strain.
It provides an objective starting point for managing absenteeism. It helps you spot patterns that might otherwise fly under the radar until they become a major headache, giving managers a chance to have supportive and timely conversations with their team members.
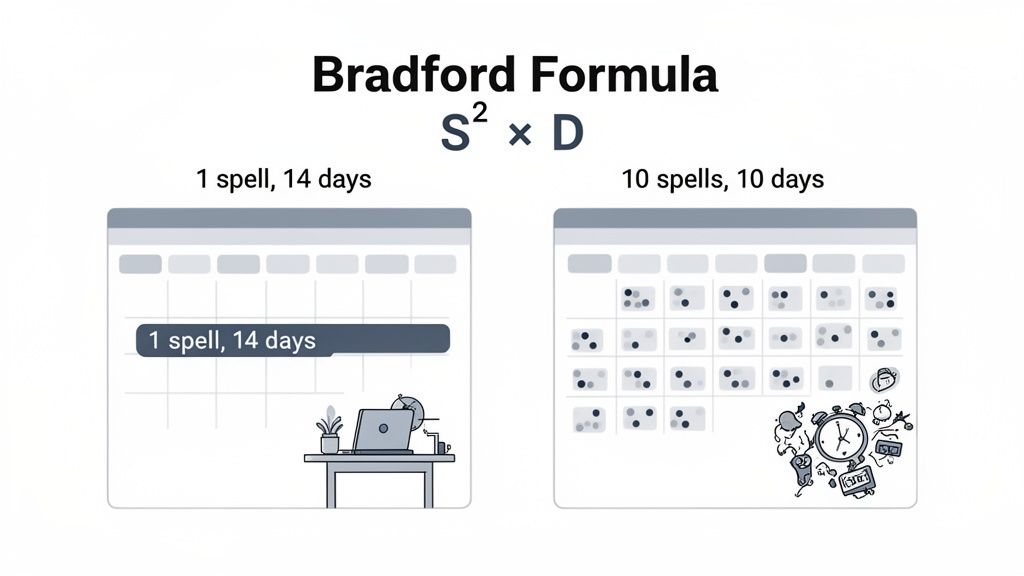
To really get to grips with how it works, here’s a quick summary of the core components.
Bradford Formula Quick Reference Guide
| Component | What It Means | Why It's Important |
|---|---|---|
| S (Spells) | The number of separate, individual instances of absence. One spell could be one day or ten consecutive days. | This is the key multiplier. Frequent spells, even if short, have a much greater impact on the score and operations. |
| D (Days) | The total number of days an employee was absent across all spells within a specific period (usually a rolling 52 weeks). | This figure provides the overall scale of the absence but is less influential on the final score than the spells. |
| S² (Spells²) | The number of spells multiplied by itself. This is the part of the formula that penalises frequency. | Squaring the spells exponentially increases the score for repeated absences, highlighting disruptive patterns. |
| Bradford Score | The final number calculated by S² x D. A higher score indicates a more disruptive pattern of absence. | This score gives HR and managers an objective data point to trigger conversations or further action. |
This table breaks down the formula into its essential parts, showing how it shifts the focus from simply counting days to understanding the frequency and impact of absenteeism.
A Brief History of the Formula
The idea isn't new; it actually came out of research in the 1980s at the Bradford University School of Management. Researchers there developed the "Bradford Factor" to measure absenteeism by focusing on the frequency of absence spells rather than just the total days taken.
In the UK, it was picked up by public sector organisations like the NHS and various local authorities, where consistent staffing is absolutely critical for delivering services.
The Bradford Formula is a specific tool for managing absence, but it sits within the wider world of HR responsibilities. For a broader look at identifying and mitigating people-related risks, this guide on risk assessment in HR is a great resource. By understanding where the formula came from, you can better apply it as part of a fair and effective attendance strategy.
How to Calculate a Bradford Score Step by Step
Knowing the theory is one thing, but actually calculating a Bradford Score is where you see the real magic happen. The formula itself is dead simple, yet it uncovers powerful insights into attendance that just counting sick days completely misses. Let’s get practical and walk through the numbers.
To do this, we'll look at two employees. This is the best way to show how two people with the exact same number of days off can have wildly different scores. It perfectly illustrates why those short, frequent absences are so disruptive.
Gather Your Data
Before you can crunch any numbers, you need two bits of information for an employee over a specific timeframe, usually a rolling 52 weeks:
- Total Spells (S): This is just the number of separate times someone was off. A single day off is one spell. Five consecutive days off for the flu is also just one spell.
- Total Days (D): This is the total number of working days the employee was absent across all those spells.
Got those two figures? Great. Now you’re ready for the formula: S² x D.
Meet Our Two Employees
Let’s bring this to life with Employee A and Employee B. They both work at the same company, and over the past year, they’ve both been off for a total of seven working days.
- Employee A (Alex): Alex had one nasty bout of flu that took him out for seven consecutive days.
- Employee B (Ben): Ben has had seven separate absences, each lasting just one day, scattered throughout the year.
On the surface, they look the same: seven days absent. But the impact on the business couldn't be more different.
Calculating the Score for Employee A
First up, let's calculate the score for Alex, who had the single long-term absence.
- Spells (S): Alex had one instance of absence, so S = 1.
- Days (D): Alex was off for a total of seven days, so D = 7.
Now, we just pop these into the Bradford Formula:
Formula: S² x D Alex's Calculation: 1² x 7 (which is 1 x 1 x 7) Alex's Bradford Score: 7
Alex's score is incredibly low. This reflects the reality of the situation: while the absence was long, it was a single, contained event that the business could plan for.
Calculating the Score for Employee B
Next, let’s run the numbers for Ben, whose absences were short but frustratingly frequent.
- Spells (S): Ben had seven separate instances of absence, so S = 7.
- Days (D): Ben was also off for seven days in total, so D = 7.
Let's see what the formula does with this pattern:
Formula: S² x D Ben's Calculation: 7² x 7 (which is 7 x 7 x 7) Ben's Bradford Score: 343
The difference is staggering. Ben’s score is almost 50 times higher than Alex's, despite them both taking the same number of days off. This is the Bradford Formula doing its job perfectly.
It mathematically proves that frequent, unpredictable absences cause far more operational chaos than one longer, planned-for period of leave. For any manager, trying to track this manually across a whole team becomes a massive headache, which is why so many turn to automated tools. You can simplify this entire process with our ultimate Bradford Score calculator guide.
Interpreting Scores with Bradford Factor Triggers
So, you've calculated a Bradford Score. What now? A score of 7 might be perfectly fine, but a score of 343 is a clear red flag. By itself, the number is just data. It becomes a powerful tool only when you have a framework for what to do next.
This is where Bradford Factor Triggers come in. Think of them as pre-agreed thresholds that prompt a specific management action. It’s a bit like a traffic light system for attendance: a low score is green (no action needed), a middling score is amber (time for a supportive chat), and a high score is red (time for a formal review).
The goal here isn't to be punitive. It’s about creating consistency. By setting clear trigger points, you ensure every employee is treated the same way, stripping out subjectivity and potential bias. It gives managers a clear, policy-driven mandate to step in at the right moment, turning what could be an awkward chat into a structured, helpful conversation.
Establishing Your Trigger Points
There are no legally defined trigger points for the Bradford Formula. It's up to each organisation to set its own based on operational needs, company culture, and the specifics of its absence policy. Over time, however, a common framework has emerged that many UK businesses use as a starting point.
This flowchart shows how the process flows from tracking absence data to calculating the final score—the number that forms the basis for applying your triggers.
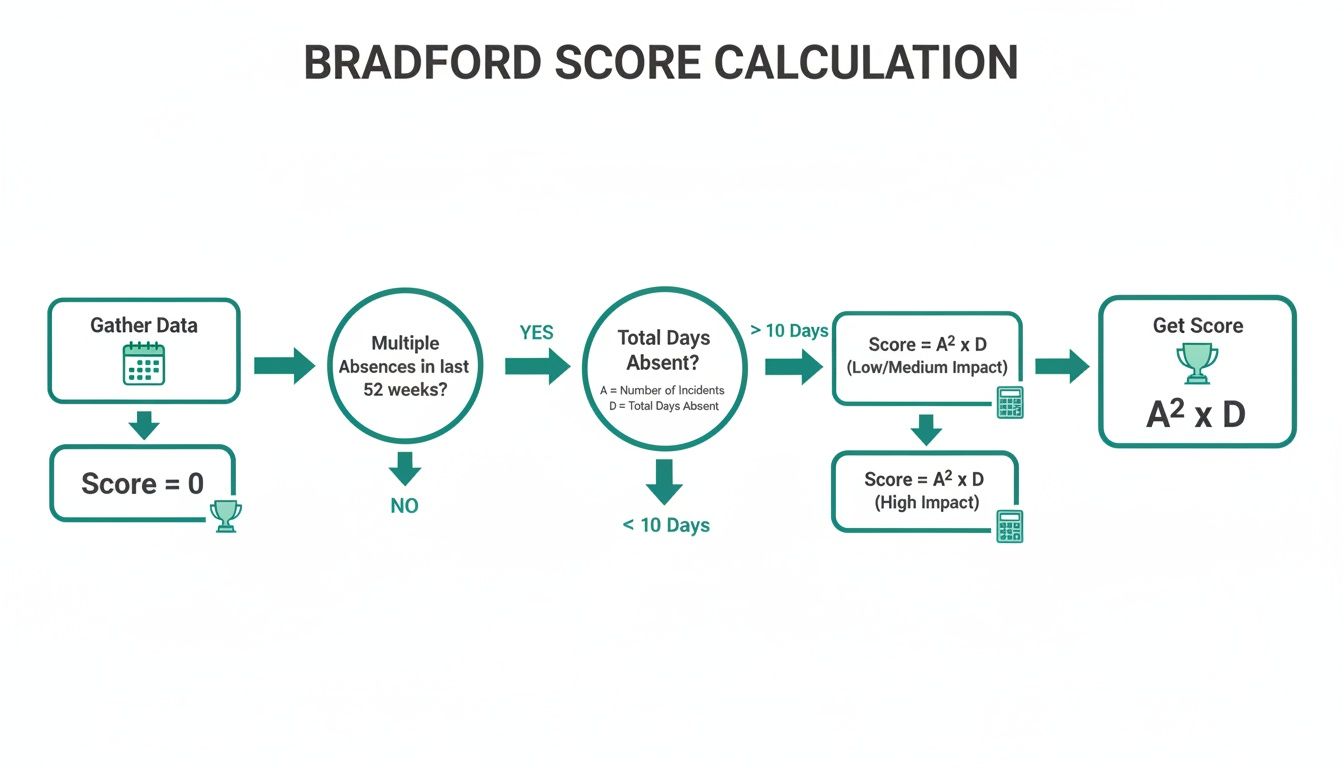
As you can see, once you have that score, the next logical step is to decide what it actually means for your business and what action, if any, it should trigger.
To give you a clearer idea, we’ve put together a table showing a common approach to linking scores with management actions. Remember, this is just an illustrative guide. Your own thresholds must be clearly defined and communicated within your company’s official absence policy.
Example Bradford Factor Trigger Points and Actions
| Bradford Score Range | Potential Action | Manager's Objective |
|---|---|---|
| 0 - 50 | No Action Required | Monitor attendance as part of standard procedure. The score indicates no disruptive pattern. |
| 51 - 200 | Informal Conversation | Have a supportive chat during a return-to-work interview to understand the reasons for the absences. |
| 201 - 400 | First Formal Written Warning | Conduct a formal meeting to discuss the impact of the absences and set clear expectations for improvement. |
| 401 - 600 | Final Written Warning | Hold a serious review, highlighting that continued high absence levels could lead to dismissal. |
| 601+ | Consideration of Dismissal | Initiate a final formal process, taking into account all circumstances and previous warnings. |
Communicating Triggers Transparently
The success of any Bradford Factor policy hinges on one thing: transparency. If your team sees it as some secretive, punitive tool, it will only damage morale and encourage "presenteeism"—where people drag themselves into work when they're genuinely ill just to avoid hitting a trigger.
To avoid this, be open about the policy from day one. Explain why you're using the formula: to maintain operational stability and ensure fairness for everyone, not to punish genuine sickness. Make sure your trigger points and the resulting actions are clearly laid out in the employee handbook.
This proactive communication builds trust and reinforces that the system is a tool for supportive conversations, not automatic discipline. To learn more, check out our guide on understanding your Bradford Factor score in our practical guide.
The Pros and Cons of Using The Bradford Formula
No HR tool is a silver bullet, and the Bradford Formula is certainly no exception. While it brings a welcome dose of standardisation to tracking absence, it's crucial to understand both its strengths and its weaknesses before you weave it into your company policies.
Think of it this way: the formula is a useful signpost, but it isn’t the entire map. Knowing what it does well—and what it can't do at all—is the key to using it effectively without falling into common traps.
The Advantages of the Bradford Formula
When you use it as intended, the Bradford Formula offers some clear wins for managing attendance and keeping the business running smoothly. It brings a level of pure objectivity to what can often feel like a very subjective and tricky conversation.
Here are its main strengths:
- It’s an Objective, Standardised Metric: The formula is just maths (S² x D). That’s it. This strips out personal bias when you're first spotting potentially disruptive absence patterns. It ensures every employee is measured against the exact same yardstick.
- It Highlights Disruptive Patterns: This is its superpower. The formula is brilliant at telling the difference between one long-term absence (like for a planned operation) and lots of short, sporadic ones. It puts a number on the sheer operational chaos that frequent, unplanned leave can cause—something a simple count of sick days completely misses.
- It Can Deter Non-Genuine Absences: Let's be honest, not every sick day is genuine. When employees know that lots of short absences will flag a high score, it can act as a deterrent. It encourages people to think twice before taking a casual day off.
- It Gives a Clear Trigger for Action: The score gives managers a clear, data-driven reason to start a conversation. This changes a potentially awkward "You've been off a lot lately" chat into a structured discussion, based on triggers you've already set out in your company policy.
The Disadvantages of the Bradford Formula
On the flip side, leaning too heavily on the Bradford Formula without applying any human context can create a whole host of problems. Its mathematical rigidity is both its greatest strength and its biggest flaw, and if you’re not careful, it can lead to unfairness and poison your company culture.
Managers and HR teams have to be switched on to these potential pitfalls:
- It Penalises Chronic Health Conditions: The formula has no heart. It can’t distinguish between reasons for absence. An employee with a recognised disability or a long-term health issue that needs regular, short appointments could be unfairly penalised for something they can't control. This is a fast track to discrimination claims under the Equality Act 2010.
- It Ignores All Context and Nuance: It treats a day off to deal with a burst pipe the same as a day off for a minor cold. Life is messy, and the formula has zero ability to consider the legitimate, often stressful, reasons someone might be absent, like caring for a sick child.
- It Can Wreck Employee Morale: If it's rolled out badly or seen as just a tool to punish people, it can breed a culture of distrust and anxiety. Employees might feel like they're constantly being watched and judged, which is a killer for morale and engagement.
- It Actively Encourages 'Presenteeism': This is perhaps the most dangerous side-effect. To avoid hitting a trigger score, employees may drag themselves into work when they are genuinely ill. Not only does this risk spreading germs to the whole team, but it also leads to rubbish productivity and much longer recovery times for the individual. While a 2019 study found that 38% of sick days taken weren't genuine, the formula can accidentally punish those who are.
Key Takeaway: The Bradford Formula should never, ever be used in isolation. It’s a tool designed to start a conversation, not to automate disciplinary action. The score is just a signal—an indicator that a supportive chat is needed to get the full story behind someone's absences.
Ultimately, how well this formula works comes down to how you apply it. If you can balance its objective data with compassionate, context-aware management, you can use it to support both your people and your business goals.
Navigating UK Legal Considerations and Best Practices
Bringing the Bradford Formula into your business isn't just a simple operational tweak. It's a decision that carries real legal weight, especially here in the UK. While the formula itself is perfectly legal, how you use it is what matters. Using it as a blunt, automated tool for discipline is a fast track to legal headaches.
The one thing to always remember is fairness. Think of the formula as a data point that should start a conversation, not deliver an automatic verdict. Without a manager’s common sense and a bit of compassion, this simple calculation can easily lead to discriminatory outcomes, putting you at risk of unfair dismissal or discrimination claims.
The Equality Act 2010 and Reasonable Adjustments
The biggest piece of legislation you need to have in mind is the Equality Act 2010. This act protects employees from discrimination based on certain "protected characteristics," including disability. This is where a rigid, one-size-fits-all application of the Bradford Formula can get you into hot water.
Imagine an employee with a recognised disability or a chronic health condition. They might rack up a high Bradford score from frequent, short absences for treatment or flare-ups. If you penalise them for these absences without digging into the underlying cause, that could easily be viewed as disability discrimination.
The law requires employers to make "reasonable adjustments" for disabled employees. In this context, that could mean discounting any disability-related absences from the Bradford calculation entirely, or perhaps adjusting the trigger points for that specific individual. Ignoring this duty is a serious misstep.
Failing to make these adjustments isn't just unfair; it's a direct breach of the Equality Act. The key is to separate absences directly linked to a protected characteristic from general sickness.
Best Practices for Fair and Lawful Application
To protect your organisation and build a culture of trust, you have to embed the Bradford Formula within a clear, fair, and consistently applied absence management policy. This policy should be your North Star, making sure every manager handles things equitably.
Here are a few essential best practices to build into your policy:
- Exclude Protected Absences: Your policy must state, in no uncertain terms, that certain absences will not be included in the Bradford score. This is non-negotiable for staying on the right side of the law.
- Communicate Everything Clearly: Make sure every single employee understands how the formula works, what the trigger points are, and what they can expect if their score is high. Transparency stops the system from feeling like some secret punishment tool.
- Train Your Managers: Your line managers are on the front line of this. They absolutely must be trained on the nuances of the policy, especially around the Equality Act, reasonable adjustments, and the importance of having supportive, confidential conversations.
- Use It as a Conversation Starter: Keep hammering home the message that a high score is a trigger for a supportive discussion, not automatic disciplinary action. The whole point is to understand the "why" behind the absences and see how you can help.
What to Exclude From the Calculation
To stay compliant and fair, your policy needs to be crystal clear about which absences are exempt from the formula.
Crucially, you must exclude absences related to:
- A known disability or long-term health condition covered by the Equality Act.
- Pregnancy-related illness.
- Any injury sustained at work.
- Pre-approved time off, like dependency leave for a family emergency.
- Authorised compassionate leave.
By thoughtfully putting these best practices into place, you can transform the Bradford Formula from a potential legal minefield into a genuinely valuable and fair tool for managing attendance. It becomes part of a supportive framework that protects both the business and its people.
Automating The Bradford Formula with Leavetrack
Calculating a Bradford Score for one or two employees is simple enough on paper. But for a growing business, the reality is a mountain of admin. Manually tracking every single absence, wrestling with spreadsheets, and recalculating scores across the entire team is a huge time drain, not to mention it’s wide open to human error.
This manual approach quickly becomes a real headache. As you scale, the risk of getting the numbers wrong goes up, and making sure every manager applies the formula fairly becomes a serious challenge. Your focus shifts from supporting your people to just managing paperwork.
![]()
This is exactly where an automated system like Leavetrack comes in. It takes the burden of manual tracking off your plate and gives managers accurate, real-time data to work with.
How Leavetrack Simplifies Absence Management
Leavetrack completely changes the game. Instead of relying on fragile spreadsheets, it gives you a central, intelligent platform that does all the heavy lifting. This frees up precious time for HR and managers to focus on what actually matters: the people behind the numbers.
Here’s a look at how it works:
- Automatic Logging: Every type of leave is logged in one place. When an employee calls in sick, the system records it, automatically keeping track of both the total days and the number of separate instances (spells).
- Real-Time Score Calculation: The platform calculates the Bradford Factor score for every employee, instantly. No need for manual formulas or remembering to update things; the scores are always current.
- Configurable Trigger Alerts: You can set your company’s specific Bradford Factor trigger points right inside the system. When an employee’s score hits a threshold, Leavetrack automatically pings the right manager, ensuring timely and consistent follow-up.
The system's clear dashboard means managers have the objective data they need for supportive return-to-work chats right at their fingertips.
The Benefits of an Automated Approach
Making the switch to an automated system brings clear, tangible benefits to the whole organisation. It's not just about saving time; it's about building a fairer, more transparent, and more efficient way of managing employee absence.
By automating the Bradford Formula, you replace administrative guesswork with data-driven clarity. This ensures every manager is equipped with accurate, objective information, leading to more consistent and fair conversations about attendance.
The advantages really stack up:
- Ensured Accuracy and Consistency: Automation gets rid of human error in the calculations. It also guarantees that the company’s absence policy is applied the same way for everyone, every time.
- Time Savings for HR and Managers: Think of all those hours spent updating spreadsheets. That time is now freed up for your team to focus on more strategic work and actually supporting employees.
- Empowered Management: Managers get objective data, giving them the confidence to hold supportive return-to-work interviews based on facts, not guesswork.
- Enhanced Visibility: Features like a central digital wall planner give you an instant overview of team availability, making it much easier to plan resources and arrange cover.
Ultimately, automation creates a solid, dependable framework. You can dive deeper into this in our guide to automated leave management systems, which explains how these tools help create a fair and transparent process for everyone involved.
Frequently Asked Questions About The Bradford Formula
Even when you get your head around the maths, putting the Bradford Formula into practice brings up a whole new set of questions. For any HR manager or business owner, navigating the tricky areas of fairness, legality, and company policy is essential if you want this tool to work for you, not against you.
Here, we’ll tackle some of the most common queries we see, giving you direct, clear answers. The goal is to help you use the formula confidently and responsibly, making it a supportive tool rather than a source of stress for your team.
Can The Bradford Formula Be Used for All Absence Types?
No, absolutely not – and this is a critical point. The formula should only be applied to unplanned, short-term sickness absences. Trying to apply it to other types of leave is a fast track to serious legal issues and claims of discrimination.
Counting protected leave towards a disciplinary score isn't just unfair; it's a massive compliance risk.
You must exclude these absences from any calculation:
- Anything related to a known disability or chronic condition protected under the Equality Act 2010.
- Pregnancy-related illnesses.
- Injuries sustained at work.
- Any kind of authorised leave, like holidays, compassionate leave, or time off for family emergencies.
Is The Bradford Formula Legal in The UK?
Yes, the formula itself is perfectly legal to use in the UK. The crunch point, however, is all in how you use it. The formula quickly becomes unlawful if it’s applied in a way that is unfair, inconsistent, or discriminatory.
For instance, if the formula triggers disciplinary action against an employee for absences linked to their disability, and you haven't made any reasonable adjustments, you would likely be in breach of the Equality Act 2010. The tool is legal; a biased application of it is not.
The key takeaway is that the formula must be just one part of a wider, supportive absence management policy. It should never be an automated system for punishment. Think of it as a trigger for a fair, considerate, and human conversation.
What Is a Good Bradford Factor Score?
There’s no magic number here. A "good" score in one company might be a major red flag in another. The right thresholds depend entirely on your organisation’s needs, your industry, and how much disruption your operations can handle.
That said, a general consensus has emerged over time. Typically, any score below 50 is seen as very low risk and doesn't need any action. Many businesses set their first trigger for an informal, supportive chat somewhere in the 125 to 200 range.
Ultimately, what’s most important is that you define your own trigger points. Document them clearly in your absence policy and make sure the whole team knows what they are. This transparency ensures everyone understands the expectations and that the process is applied consistently to all.
Ready to stop wrestling with spreadsheets and start managing absence with clarity and confidence? Leavetrack automates Bradford Score calculations, provides real-time insights, and empowers your managers to have supportive, data-driven conversations. See how much time you could save by visiting https://leavetrackapp.com.
